수정입니다
Bottom-up Parsing 본문
Bottom - up parsing - reverse of right most derivation
- The parsing problem is finding the correct RHS in a right sentential form to reduce to get the previous right sentential form in the derivaton.
- 주어진 input 에서 시작 -> 시작 기호(여기서 E)만 남을 때까지 sequence 생성
- 각 단계에서 이전 sentential form을 얻기 위해 특정 RHS(handle)을 찾아야함
- right sentential form 에서 handle은 unique 하다.
ex) id + id * id
E -> E + T | T
T -> T * F | F
F -> (E) | id
rightmost derivation
E => E+T => E+T*F => E+T*id => E+F*id => E+id*id => T+id*id => F+id*id
=>id+id*id
reverse of rightmost derivation
id+id*id
=> F+id*id
=>T+id*id
=>E+id*id
=>E+F*id
=>E+T*id // 여기서 E+T*id 는 E*id or E+T*F 두가지 선택지가 있다.
=>E+T*F // E*id는 올바른 문장형태가 아니므로 로 E+T*F 선택, 이 때 id가 handle
=>E+T
=>E
*틈새 리마인드
terminal symbol - a,b,c .... 시작부분 소문자
nonterminal symbol - A,B,C .... 시작부분 대문자
terminal or nonterminal - ... W,X,Y,Z 끝부분 대문자
terminal로 구성된 문자열 - ... w, x, y, z 끝부분 소문자
혼합문자열(ter or nonter) - α, β, δ, γ ... 그리스 소문자들
Definition of Handle

솔직히 뭔 말인지 잘 모르겠음ㅋㅋ
그냥 직관으로 이해하자면 Def1은 어떤 nonterminal A가 다른 어떤 문자열로 변하는 순간 그 β를 handle이라고 한다..
그리고 그 β (handle)는 phrase 일 수도, simple phrase 일 수도 있는데 , 그 차이는 derivation을 여러번 하냐 or 딱 한번만 하냐로 갈린다.
phrase : 전체 parse tree의 한 개의 특정 중간 노드를 루트로 하는 sub tree의 모든 leaf node
simple phrase : 그 루트 nonterminal로부터 딱 한 단계의 derivation만 거친 phrase
위 사진
E => E + T => E + T * F => E + T* id
- root node
- phrase - phrase들은 반드시 주어진 문법의 RHS 일 필요는 없다
- simple phrase - 얘는 항상 문법의 RHS
어떤 right sentential form 의 handle은 그 문장의 leftmost 에 위치한 simple phrase이다.
LL parser(Left to right , Lightmost parser) - top-down
- production과 input을 비교함
- production에서 leftmost derivation을 진행하면서 input과 match 되는 것이 있으면 양 쪽에서 지운다
- production, input이 모두 match되어 사라지면 accept (아니면 에러)
LR parser(Left to right , Rightmost parser) - bottom-up
- shift : input의 next token을 buffer에 넣음
- buffer에서 handle을 찾아서 nonterminal로 reduce함
- buffer에 시작 symbol만 남으면 accept
해보자
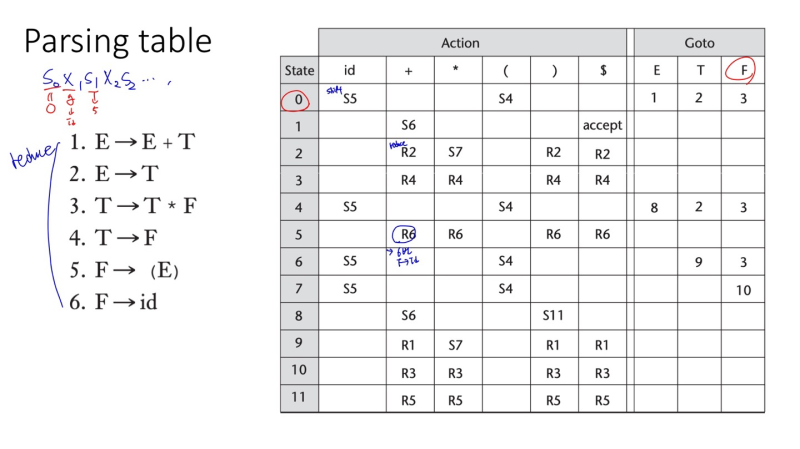
이 parsing table은 그냥 어디서 자동으로 만들어 주는 것
id + id * id를 파싱 해봅시다
|
stack
|
input
|
action
|
|
0
|
id + id *id$
|
shift 5
|
|
0id5
|
+ id * id$
|
reduce6(use GOTO[0,F])
|
|
0F3
|
+ id * id$
|
reduce4(use GOTO[0,T])
|
|
0T2
|
+id*id$
|
reduce2(use GOTO[0,E])
|
|
0E1
|
+id*id$
|
shift6
|
|
0E1+6
|
id*id$
|
shift5
|
|
0E1+6id5
|
*id$
|
reduce6(use GOTO[6,F])
|
|
0E1+6F3
|
*id$
|
reduce4(use GOTO[6,T])
|
|
0E1+6T9
|
*id$
|
shift7
|
|
0E1+6T9*7
|
id$
|
shift5
|
|
0E1+6T9*7id5
|
$
|
reduce6(use GOTO[7,F])
|
|
0E1+6T9*7F10
|
$
|
reduce3(use GOTO[6,T]
|
|
0E1+6T9
|
$
|
reduce1(use GOTO[0,E])
|
|
0E1
|
$
|
accept
|
생각보다 복잡하다
헷갈리는 부분 보면서 간단한 예시
이전 action인 reduce6(use GOTO[7,F]) 를 보고
0E1+6T9*7id5 이걸 reduce 6 (6번 문법 : F->id) 을 해줌 == 0E1+6T9*7F
이후에 GOTO 테이블의 7(현재 최우측 state 번호) , F(reduce 해서 만들 nonterminal) 를 확인하면 10이라는 숫자가 있음
그럼 reduce하고 남은 0E1+6T9*7F에 10을 붙여서 다음 stack에 넣어줌
|
0E1+6T9*7F10
|
$
|
reduce3(use GOTO[6,T]
|
|
0E1+6T9
|
$
|
reduce1(use GOTO[0,E])
|
0E1+6T9*7F10 까지 왔으면, 이제 state 번호 10이랑 next token $를 보고 다음 action을 테이블에서 찾아줌
-> R3 : reduce3 (T->T*F)
여기서 주의. .T*F 를 한꺼번에 없애는거라서,
reduce 후 남은 stack은 0E1+6 이다. 이후에 GOTO[6,T](최우측 state 6, reduce nonterminal T)로 가면 9를 찾을 수 있음
그러니까
0E1+6T9*7F10 여기서
0E1+6T9 이게 되는건
사실은
0E1+6T9*7F10
0E1+6
0E1+6T9
* 그냥 0E1+6T9*7 이렇게 생각해버리면 최우측 state # 가 7이라서 GOTO[7,T] 이 되는데, table에 그 정보는 없다.
정리하자면
state 번호 + next token 확인 후 action table에서 뭐 해야되는지 찾기
action(shift, reduce) 시키는대로 하고, 곁다리 숫자 꼭 붙여서 stack에 다시 넣기
이걸 accept 할 때까지 반복
Shift - Reduce Algorithms
- reduce is the action of replacing the handle on the top of the parse stack with its correspondig LHS
- shift is the action of moving the next token to the top of the parse stack
Advantages of LR parsers:
- They will work for nearly all grammars that describe any programming L
- They work on a larger class of grammars than other bottom-up algorithms, but are as efficient as any other bottom-up parser
- They can detect syntax errors as soon as it is possible (more faster than top-down)
- The LR class of grammars is a superset of the class parsable by LL parsers.
- LL로 파싱 x 인것들을 LR로 가능 - > 더 많이 쓴다.
LR parsers must be constructed with a tool
- parsing table 말하는 거
Knuth's insight
: 입력 문자열의 길이, 문장 형태의 길이, 파서 스택의 깊이와 상관없이, 파싱 과정에 관련되는 상대적으로 작은 개수의 다른 상황들만이 존재한다는 것을 발견
- 각 상황은 state로 표현되어서 parser stack의 꼭대기에 에 저장된다 (위에서 계속 쓴 state number)
LR parser
- ACTION table
--> 주어진 parser state와 next token을 이용해서 action을 특정한다
- GOTO table
--> reduction action이 일어난 후에, 어떤 state 가 stack의 top에 들어갈 것인지 알려줌
Parser actions:
Shift
- input의 next symbol이 stack 에 pushed
- action table에 특정 되어있는 state symbol도 next symbol 뒤에 같이 따라 붙음
Reduce
- handle이랑 그 state symbol이랑 같이 stack에서 지움
- 문법이 만드는 LHS를 stack에 넣고 GOTO table에서 state symbol도 뒤에 같이 넣음
Accept -> the parse is complete and no errors were found
Error -> the parse calls an error-handling routine
A parser table can generated form a given grammar with a tool
ex) yacc or bison
// end of chapter 4
'전공 > 프로그래밍언어론' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Expressions and Assignment Statements (1) | 2023.12.28 |
|---|---|
| Data types(2) - record, tuple, list, union, pointer, type checking (0) | 2023.12.28 |
| Data Types(1) - numeric, string, array (1) | 2023.12.28 |
| Name, Bindings, and Scope(2) - Scope (0) | 2023.12.28 |
| Name, Bindings, and Scope(1) - Name, Bindings (0) | 2023.12.28 |


