수정입니다
Data Types(1) - numeric, string, array 본문
Chapter 6. Data Types
Introduction
- data type은 data objects 의 모임과 그 값들에 대한 predefined operations의 집합을 정의한다
- descriptor는 변수들의 속성의 모임이다
- object란 user-defined type의 instance를 의미한다
- One design issue for all data types
--> What operatons are defined and how are they specified?
Primitive Data types
- 대부분의 PL들이 제공하는 기본 데이터 타입 ex) int, char..
- 다른 type들의 관점에서는 정의되지 않은 type 을 primitive data type이라 한다.
- 어떤 primitive data types은 그냥 hardware의 반영이다 - 대부분의 정수 타입
ex) 32bit 컴퓨터에서의 int는 32bit고, 64bit에서는 64bit임
- 다른 primitive data type은 약간의 nonhardeware적 지원이 필요하다
Numeric type
- int, float, double, sign, unsign...
- 몇몇 초기의 PL들은 이 numeric type만 제공함
- Integer
- 가장흔한 primitive numeric data type
- 현재 많은 컴퓨터들이 다양한 크기의 integer를 지원함
- Java : byte, short, int, long
- C++ , C# : unsigned integer 포함
- Floating point
- real number를 모델링 하지만, 정확한 값 표현 x, 근사값일뿐임
- 대부분 float, double 두가지를 지원함
- double-precision variable은 보통 float 보다 두 배 정도의 storage를 차지하고, 적어도 두 배 정도의 bit 개수를 제공한다.
- IEEE Floating-Point Standard 754 를 많이 씀 (컴구에서 배운 그거)
- Complex(복소수)
- Fortran, Python이 지원함
- python에서는 (7 + 3j) 이런 식으로 표현함 (허수 표현은 원래 i 지만 j로 쓴다)
- Decimal
- business applications 분야를 지원하기 위해 설계됨 - COBOL에서 필수적
- C#, F#도 이 type을 지원함
- 장점 : 제한된 범위에 포함된 십진수 값들을 정확하게 저장할 수 있음
(0.1 은 decimal로 정확히 표현할 수 있지만, floating point로는 불가능함)
- 단점 : limited range(지수가 허용되지 않아서), wastes memory(binary보다 많은 storage 차지)
- Boolean
- 가장 단순한 type
- true or false 딱 두개의 element를 가짐
- 1개의 bit로 표현이 가능하지만, 많은 machine에서 single bit of memory에 효율적으로 접근할 수 없기 때문에 효율적으로 addressing이 가능한 byte 에 저장된다. (가장 작은 memory cell 단위)
- 장점 : readability
- Character
- numeric coding으로 저장된다
- 가장 공통적으로 사용되는 기법 : 8-bit code ASCII (0~127 값에 서로 다른 char 저장)
- 16-bit coding : Unicode(UCS-2)
--> 세상에 존재하는 대부분의 자연 언어를 포함함
--> Java 가 가장 먼저 사용
--> 이후 많은 언어들에 차용됨
- 32-bit Unicode(UCS-4, UTF-32)
--> 2003년부터 Fortran 에서 지원됨
Character String Types
- sequences of characters
- Design issues
--> Is it a primitive type or just a special kind of array? (C++ : string은 class지 기본타입 x)
--> Should the length of strings be static or dynamic?
Character String Types Operations
- Assignment and Copying
- Comparison(=, >, etc.)
- Catenation('a' + 'b' = 'ab')
- Substring reference
- Pattern matching
Character String Type in Certain Languages
- C, C++ -> char array를 통해 character string 저장
--> Not primitive
--> char str[] = "apples" , str = apples\0 ( 문자열이 null로 끝남)
--> + library 를 통해 string operation 제공
- SNOBOL4 (a string manipulation language)
--> Primitive
--> many operation, pattern matching 포함
- Fortran , Python
--> Primitive type with assignment and several operations
- Java(C#, Ruby, swift)
--> Primitive via the String class
- Perl, JavaScript, Ruby, PHP
--> provide built-in pattern matching, using regular expressions
Character String Length Options
- Static : COBOL, Java's String class
- Limited Dynamic Length : C, C++
--> null문자를 사용해서 문자의 끝을 나타냄
--> 제한된 길이 내에서 문자 길이를 자유롭게 조정 가능
- Dynamic(no maximum) : SNOBOL4, Perl, JavaScript
** char a[10]; a = "apple";
static -> a p p l e 0 0 0 0 0 : Length 10
char a[]; a = "apple";
limited dynamic -> a p p l e \0 : length 5(strlen) or 6(sizeof)
Character String Type Evaluation
- 언어의 writability에 중요하다
- string 을 기본 타입으로 제공하는게 훨씬 편리함.. 비싸지도 않음
- dynamic은 좋지만, 비싸다
Character String Implementation
- static length : compile time descriptor
static string
Length
Address
- limited dynamic length : run time descriptor
Limited dynamic string
Maximum length
Current length
Address
--> C, C++은 필요 없다 (null 문자로 구분 해주고 있어서)
- dynamic length : run time descriptor(using heap)
--> 더 복잡한 stroage 요구(길이에 따라 공간이 와리가리)
--> alloc/dealloc 문제
Enumeration Types
- All possible values, which are named constants, are provided in the definition
ex) c#
--> default 적으론, mon부터 0, 1, 2 .. 순서대로 정수 값 할당
--> mon = 1, tue = 3 ... 이렇게도 지정 가능
- Design issues
--> Is an enumeration constant allowed to appear in more than one type definition, and if so, how is the type of an occurrence of that constant checked?
--> Are enumeration values coerced to integer?
--> Any other type coerced to an enumeration type?
ex) c++
c++에서 임의의 numeric type으로 enum value가 할당되는 거 허용함
근데 color white = 2 같이 다른 type 값이 enum type으로 변환되는거 허용 안함(casting 해야됨)
c++ 에서는 same name, different type을 허용 안함 (overloaded literals)
( 위 예시에서 signal 에 red가 들어가 있다면 충돌이라고 에러 난다)
대신 Ada에서는 허용함.
Evaluation of Enumerated Type
- readability : no need to code a color as a number
- reliability : compiler can check
--> enum type에 산술 연산 불가능
--> No enumeration variable can be assigned a value outside its defined range
Array Types
- homogeneous aggregate of data elements
- homogeneous : all elements should have same data type
- element들은 첫번째 element랑 비교해서 relative한 위치를 갖는다(not absolute)
- 각각의 element의 주소는 indexing같은 subscript expression에 의해 특정된다.
Array design issues
- What types are legal for subscripts?
- Are subscripting expressions in element reference range checked?
--> depends on PL, its error or warning..
- When are subscript ranges bound?(related to size of array)
- When does allocation take place?(static or dynamic)
- Are ragged or rectangular multidimensional arrays allowed, or both?
--> ragged : 2차원 배열일 때, 각 1차원 배열이 같은 사이즈
--> rectangular : 2차원 배열일 때, 각 1차원 배열이 다른 사이즈
- What is the maximum number of subscripts?
- Can array object be initialized?
- Are any kind of slices supported?(using the indexing)
Array Indexing
- Indexing(or subscripting) is mapping from indices to elements
- Index syntax
--> Fortran, Ada use parentheses ()
(Ada 에서 소괄호를 선택한 이유가 array reference랑 function call 사이의 uiformity을 위해서래.. 둘다 mapping이라.. 뭔소리니.. 그니까 함수 A 호출할 때 A() 하는거랑 array b를 참조할 때 b(1)이렇게 하는거랑 어쨌든 둘다 mapping이라 그 균일성이 만들기 위해(?))
--> most other use brakets []
Subscript Binding and Array Categories
- Static : subscript 범위랑 storage 할당이 static 함(run time 전에)
--> 장점 : time efficiency
- Fixed stack-dynamic : 범위는 static하게 결정, 할당은 dynamic으로(run time에)
--> 장점 : space efficiency
- Fixd heap-dynamic : 위랑 비슷, 차이점은 binding이 사용자가 요청했을 때 일어난다는 점과, 할당이 stack이 아닌 heap에 된다는 점
- heap-dynamic : 범위랑 할당 둘다 dynamic하게 언제든지 바뀔 수 있음
장점 --> flexibility
Subscript Binding and Array Categories
- C, C++
--> static 포함 : static
--> static 포함 x : fixed stack-dynamic
--> new, malloc.. : fixed heap-dynamic
- Perl, JavaScript, Python, Ruby support heap-dynamic arrays
Array Initialization
- C, C++, Java, Swift, C#
--> storage allocation 되는 시점에 초기화 허용
ex)
Heterogeneous Arrays
- array element끼리 type 다른거 허용
- Perl, Python, JavaScript, Ruby
Arrays Operations
- APL provides the most powerful array processing operations for vectors and matrixes as well as unary operators(ex/ to reverse column elements)
- Python's array assignments, but they are only reference changes
- Python supports array catenation(+) & element membership operations(in)
- Ruby also provides array catenation
Rectangular and Jagged Arrays
- C, C++, Java : jagged
- F#, C# : rec + jag 둘다
Slices
- some substructure of an array (단순히 배열의 한 부분을 참조)
- slices are only useful in languages that have array operations
ex) python
ex) Ruby
Implementation of Array
- list[k]
- address(list[k]) = address(list[lower_bound]) + ((k - lower_bound) * element_size)
-> k가 4면 list[4]의 주소값은 list[0] + 4 * sizeof(anytype)
Accessing Multi-demensioned Arrays
- 두가지 방법
- Row major order(by rows) - used in most languages
- Column major order(by columns) - used in Fortran
Locating an Element in a Multi-dimensioned Array
- General format
Location(a[i,j]) = address of a[row_lb, col_lb] + (((i - row_lb) * n) + (j - col_lb)) * elemnet_size
Compile time Descriptor
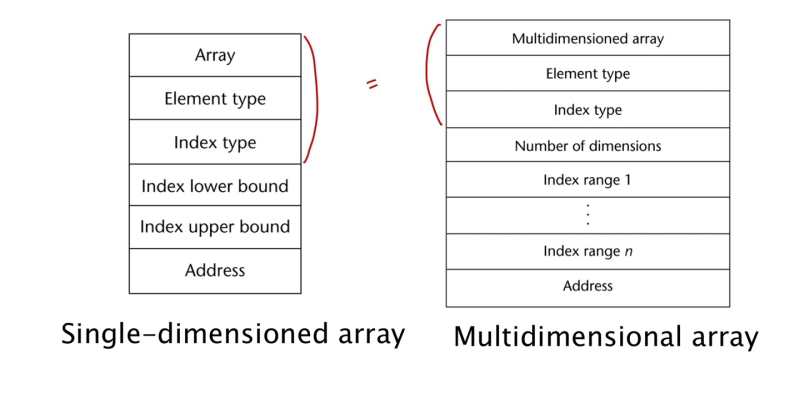
Associative Arrays
- unordered collection of data elements
- ex) dictionary
- key 로 indexing 됨
--> user-defined keys must be stored
--> 이거 아니면 regularity 때문에 stored 될 필요 없음
- Design issues
--> What is the form of references of elements?
--> Is the size static or dynamic?
- Built-in type : Perl, Python, Ruby, Swift
- In Perl
'전공 > 프로그래밍언어론' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Expressions and Assignment Statements (1) | 2023.12.28 |
|---|---|
| Data types(2) - record, tuple, list, union, pointer, type checking (0) | 2023.12.28 |
| Name, Bindings, and Scope(2) - Scope (0) | 2023.12.28 |
| Name, Bindings, and Scope(1) - Name, Bindings (0) | 2023.12.28 |
| Bottom-up Parsing (0) | 2023.12.28 |

